- Belarus
-
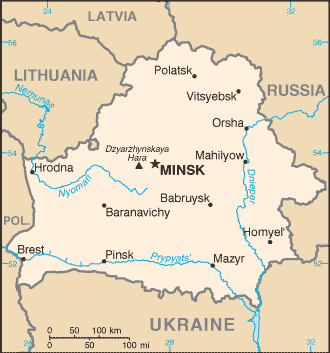 Introduction ::BelarusBackground:After seven decades as a constituent republic of the USSR, Belarus attained its independence in 1991. It has retained closer political and economic ties to Russia than any of the other former Soviet republics. Belarus and Russia signed a treaty on a two-state union on 8 December 1999 envisioning greater political and economic integration. Although Belarus agreed to a framework to carry out the accord, serious implementation has yet to take place. Since his election in July 1994 as the country's first president, Aleksandr LUKASHENKO has steadily consolidated his power through authoritarian means. Government restrictions on freedom of speech and the press, peaceful assembly, and religion remain in place.Geography ::BelarusLocation:Eastern Europe, east of PolandGeographic coordinates:53 00 N, 28 00 EArea:total: 207,600 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 86land: 202,900 sq kmwater: 4,700 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly smaller than KansasLand boundaries:total: 3,306 kmborder countries: Latvia 171 km, Lithuania 680 km, Poland 605 km, Russia 959 km, Ukraine 891 kmCoastline:0 km (landlocked)Maritime claims:none (landlocked)Climate:cold winters, cool and moist summers; transitional between continental and maritimeTerrain:generally flat and contains much marshlandElevation extremes:lowest point: Nyoman River 90 mhighest point: Dzyarzhynskaya Hara 346 mNatural resources:timber, peat deposits, small quantities of oil and natural gas, granite, dolomitic limestone, marl, chalk, sand, gravel, clayLand use:arable land: 26.63%permanent crops: 0.59%other: 72.78% (2011)Irrigated land:1,150 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:58 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 4.34 cu km/yr (32%/65%/3%)per capita: 435.4 cu m/yr (2009)Natural hazards:NAEnvironment - current issues:soil pollution from pesticide use; southern part of the country contaminated with fallout from 1986 nuclear reactor accident at Chornobyl' in northern UkraineEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:landlocked; glacial scouring accounts for the flatness of Belarusian terrain and for its 11,000 lakesPeople and Society ::BelarusNationality:noun: Belarusian(s)adjective: BelarusianEthnic groups:Belarusian 83.7%, Russian 8.3%, Polish 3.1%, Ukrainian 1.7%, other 3.2% (2009 census)Languages:Belarusian (official) 23.4%, Russian (official) 70.2%, other 6.4% (includes small Polish- and Ukrainian-speaking minorities) (1999 census)Religions:Eastern Orthodox 80%, other (including Roman Catholic, Protestant, Jewish, and Muslim) 20% (1997 est.)Population:9,625,888 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 90Age structure:0-14 years: 15.2% (male 752,536/female 710,384)15-24 years: 12.3% (male 607,877/female 575,827)25-54 years: 45.5% (male 2,146,332/female 2,238,033)55-64 years: 13% (male 548,170/female 699,780)65 years and over: 14% (male 423,287/female 923,662) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 41.1 %youth dependency ratio: 21.6 %elderly dependency ratio: 19.5 %potential support ratio: 5.1 (2013)Median age:total: 39.2 yearsmale: 36.1 yearsfemale: 42.2 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:-0.18% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 211Birth rate:10.99 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 175Death rate:13.68 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 13Net migration rate:0.85 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Urbanization:urban population: 75% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 0.21% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:MINSK (capital) 1.861 million (2011)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.96 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.78 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.46 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.87 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:24.9 (2010 est.)Maternal mortality rate:190 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 58Infant mortality rate:total: 3.67 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 206male: 4.1 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 3.22 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 71.81 yearscountry comparison to the world: 140male: 66.14 yearsfemale: 77.82 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:1.46 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 193Contraceptive prevalence rate:72.6% (2005)Health expenditures:5.6% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 119Physicians density:4.87 physicians/1,000 population (2007)Hospital bed density:11.1 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 99% of populationtotal: 100% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 1% of populationtotal: 0% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 91% of populationrural: 97% of populationtotal: 93% of populationunimproved:urban: 9% of populationrural: 3% of populationtotal: 7% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.3% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 82HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:17,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 82HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 1,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Obesity - adult prevalence rate:24.3% (2008)country comparison to the world: 65Children under the age of 5 years underweight:1.3% (2005)country comparison to the world: 126Education expenditures:5.3% of GDP (2011)country comparison to the world: 62Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 99.6%male: 99.8%female: 99.5% (2009 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 15 yearsmale: 15 yearsfemale: 16 years (2011)Child labor - children ages 5-14:total number: 54,218percentage: 5 % (2005 est.)Government ::BelarusCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Belarusconventional short form: Belaruslocal long form: Respublika Byelarus'local short form: Byelarus'former: Belorussian (Byelorussian) Soviet Socialist RepublicGovernment type:republic in name, although in fact a dictatorshipCapital:name: Minskgeographic coordinates: 53 54 N, 27 34 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)daylight saving time: none scheduled for 2013Administrative divisions:6 provinces (voblastsi, singular - voblasts') and 1 municipality* (horad); Brest, Homyel' (Gomel), Horad Minsk* (Minsk City), Hrodna (Grodno), Mahilyow (Mogilev), Minsk, Vitsyebsk (Vitebsk)note: administrative divisions have the same names as their administrative centers; Russian spelling provided for reference when different from BelarusianIndependence:25 August 1991 (from the Soviet Union)National holiday:Independence Day, 3 July (1944); note - 3 July 1944 was the date Minsk was liberated from German troops, 25 August 1991 was the date of independence from the Soviet UnionConstitution:15 March 1994; revised by national referendum 24 November 1996 giving the presidency greatly expanded powers; became effective 27 November 1996; revised again 17 October 2004 removing presidential term limitsLegal system:civil law system; note - nearly all major codes (civil, civil procedure, criminal, criminal procedure, family and labor) have been revised and came into force in 1999 or 2000International law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: president Aleksandr LUKASHENKO (since 20 July 1994); note - the US does not recognize the results of the 19 December 2010 elections under which the Central Election Commission of Belarus declared LUKASHENKO presidenthead of government: prime minister Mikhail MYASNIKOVICH (since 28 December 2010); first deputy prime minister Vladimir SEMASHKO (since December 2003)cabinet: Council of Ministers(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term; first election took place on 23 June and 10 July 1994; according to the 1994 constitution, the next election should have been held in 1999, however, Aleksandr LUKASHENKO extended his term to 2001 via a November 1996 referendum; subsequent election held on 9 September 2001; an October 2004 referendum ended presidential term limits and allowed the president to run in a third (19 March 2006) and fourth election (19 December 2010); prime minister and deputy prime ministers appointed by the presidentelection results: Aleksandr LUKASHENKO reelected president; percent of vote - Aleksandr LUKASHENKO 79.7%, Andrey SANNIKOV 2.6%, other candidates 17.7%; note - election marred by electoral fraudLegislative branch:bicameral national assembly or natsionalnoye sobraniye consists of the Council of the Republic or Sovet Respubliki (64 seats; 56 members elected by regional and Minsk city councils and 8 members appointed by the president, to serve four-year terms) and the Chamber of Representatives or Palata Predstaviteley (110 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms); note - the US does not recognize the legitimacy of the national assemblyelections: Palata Predstaviteley - last held on 23 September 2012 (next to be held September 2016); OSCE observers determined that the election was neither free nor impartial and that vote counting was problematic in a number of polling stations; pro-LUKASHENKO candidates won every seat with no opposition representation in the chamber; international observers determined that the previous election, on 28 September 2008, despite minor improvements also fell short of democratic standards, with pro-LUKASHENKO candidates winning every seatelection results: Sovet Respubliki - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; Palata Predstaviteley [2008] - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - KPB 6, AP 1, no affiliation 103; Palata Predstaviteley [2012] - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - KPB 3, AP 1, no affiliation 106Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the chairman, deputy chairman, and NA judges); Constitutional Court (consists of 12 judges including a chairman and deputy chairman)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the president with the consent of the Council of the Republic; judges initially appointed for 5 years and evaluated for life appointment; Constitutional Court judges - 6 appointed by the president and 6 elected by the Chamber of Representatives; term of judges is 11 years with an age limit of 70subordinate courts: regional, district, city, town, and military courtsPolitical parties and leaders:pro-government parties:Belarusian Agrarian Party or AP [Mikhail SHIMANSKY]Belarusian Patriotic Movement (Belarusian Patriotic Party) or BPR [Nikolay ULAKHOVICH, chairman]Communist Party of Belarus or KPB [Igor KARPENKO]Liberal Democratic Party or LDP [Sergey GAYDUKEVICH]Republican Party of Labor and Justice [Vasiliy ZADNEPRYANYY]opposition parties:Belarusian Christian Democracy Party [Pavel SEVERINETS] (unregistered)Belarusian Party of the Left ""Fair World"" [Sergey KALYAKIN]Belarusian Popular Front or BPF [Aleksey YANUKEVICH]Belarusian Social-Democratic Hramada [Stanislav SHUSHKEVICH]Belarusian Social Democratic Party Hramada (""Assembly"") or BSDPH [Irina VESHTARD]Belarusian Social Democratic Party People's Assembly (""Narodnaya Hramada"") [Nikolay STATKEVICH] (unregistered)Christian Conservative Party or BPF [Zyanon PAZNIAK]European Belarus Campaign [Andrey SANNIKOV]Party of Freedom and Progress [Vladimir NOVOSYAD] (unregistered)""Tell the Truth"" Campaign [Vladimir NEKLYAYEV]United Civic Party or UCP [Anatoliy LEBEDKO]Political pressure groups and leaders:Assembly of Pro-Democratic NGOs (unregistered) [Sergey MATSKEVICH]Belarusian Congress of Democratic Trade Unions [Aleksandr YAROSHUK]Belarusian Association of Journalists [Zhana LITVINA]Belarusian Helsinki Committee [Aleh HULAK]Belarusian Independence Bloc (unregistered) and For Freedom movement [Aleksandr MILINKEVICH]Belarusian Organization of Working Women [Irina ZHIKHAR]BPF-Youth [Andrus KRECHKA]Charter 97 (unregistered) [Andrey SANNIKOV]Perspektiva small business association [Anatol SHUMCHENKO]Nasha Vyasna (unregistered) (""Our Spring"") human rights center [Ales BYALYATSKI]""Tell the Truth"" Movement [Vladimir NEKLYAYEV]Women's Independent Democratic Movement [Ludmila PETINA]Young Belarus (Malady Belarus) [Zmitser KASPYAROVICH]Youth Front (Malady Front) [Zmitser DASHKEVICH]International organization participation:BSEC (observer), CBSS (observer), CEI, CIS, CSTO, EAEC, EAPC, EBRD, FAO, GCTU, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, NSG, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, PFP, SCO (dialogue member), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer), ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Oleg KRAVCHENKOchancery: 1619 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20009telephone: [1] (202) 986-1604FAX: [1] (202) 986-1805consulate(s) general: New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Ethan GOLDRICHembassy: 46 Starovilenskaya Street, Minsk 220002mailing address: PSC 78, Box B Minsk, APO 09723telephone: [375] (17) 210-12-83FAX: [375] (17) 234-7853Flag description:red horizontal band (top) and green horizontal band one-half the width of the red band; a white vertical stripe on the hoist side bears Belarusian national ornamentation in red; the red band color recalls past struggles from oppression, the green band represents hope and the many forests of the countryNational symbol(s):mounted knight known as Pahonia (the Chaser)National anthem:name: ""My, Bielarusy"" (We Belarusians)lyrics/music: Mikhas KLIMKOVICH and Uladzimir KARYZNA/Nester SAKALOUSKInote: music adopted 1955, lyrics adopted 2002; after the fall of the Soviet Union, Belarus kept the music of its Soviet-era anthem but adopted new lyrics; also known as ""Dziarzauny himn Respubliki Bielarus"" (State Anthem of the Republic of Belarus)Economy ::BelarusEconomy - overview:As part of the former Soviet Union, Belarus had a relatively well-developed industrial base; it retained this industrial base - which is now outdated, energy inefficient, and dependent on subsidized Russian energy and preferential access to Russian markets - following the breakup of the USSR. The country also has a broad agricultural base which is inefficient and dependent on government subsidies. After an initial burst of capitalist reform from 1991-94, including privatization of state enterprises, creation of institutions of private property, and development of entrepreneurship, Belarus' economic development greatly slowed. About 80% of all industry remains in state hands, and foreign investment has been hindered by a climate hostile to business. A few banks, which had been privatized after independence, were renationalized. State banks account for 75% of the banking sector. Economic output, which had declined for several years following the collapse of the Soviet Union, revived in the mid-2000s thanks to the boom in oil prices. Belarus has only small reserves of crude oil, though it imports most of its crude oil and natural gas from Russia at prices substantially below the world market. Belarus exported refined oil products at market prices produced from Russian crude oil purchased at a steep discount. In late 2006, Russia began a process of rolling back its subsidies on oil and gas to Belarus. Tensions over Russian energy reached a peak in 2010, when Russia stopped the export of all subsidized oil to Belarus save for domestic needs. In December 2010, Russia and Belarus reached a deal to restart the export of discounted oil to Belarus. Little new foreign investment has occurred in recent years. In 2011, a financial crisis began, triggered by government directed salary hikes unsupported by commensurate productivity increases. The crisis was compounded by an increased cost in Russian energy inputs and an overvalued Belarusian ruble, and eventually led to a near three-fold devaluation of the Belarusian ruble in 2011. In November 2011, Belarus agreed to sell to Russia its remaining shares in Beltransgaz, the Belarusian natural gas pipeline operator, in exchange for reduced prices for Russian natural gas. Receiving more than half of a $3 billion loan from the Russian-dominated Eurasian Economic Community Bail-out Fund, a $1 billion loan from the Russian state-owned bank Sberbank, and the $2.5 billion sale of Beltranzgas to Russian state-owned Gazprom helped stabilize the situation in 2012; nevertheless, the Belarusian currency lost more than 60% of its value, as the rate of inflation reached 53% in 2011 and 59% in 2012.GDP (purchasing power parity):$149.2 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 63$147 billion (2011 est.)$139.2 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$63.26 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:1.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1475.5% (2011 est.)7.7% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$15,900 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 85$15,600 (2011 est.)$14,700 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:31.6% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2029.2% of GDP (2011 est.)26.2% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 46.7%government consumption: 14.6%investment in fixed capital: 32.8%investment in inventories: 1.6%exports of goods and services: 81.6%imports of goods and services: -77.1%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 9.1%industry: 47.2%services: 43.7% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:grain, potatoes, vegetables, sugar beets, flax; beef, milkIndustries:metal-cutting machine tools, tractors, trucks, earthmovers, motorcycles, televisions, synthetic fibers, fertilizer, textiles, radios, refrigeratorsIndustrial production growth rate:4% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Labor force:5 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 76Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 9.4%industry: 45.9%services: 44.7% (2005 est.)Unemployment rate:1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 71.6% (2005)note: official registered unemployed; large number of underemployed workersPopulation below poverty line:27.1% (2003 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 3.8%highest 10%: 21.9% (2008)Distribution of family income - Gini index:27.2 (2008)country comparison to the world: 12521.7 (1998)Budget:revenues: $22.38 billionexpenditures: $21.96 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:35.4% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):0.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 34Public debt:31.5% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 11448.5% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):59.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 22353.3% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:10.5% (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 1413.5% (31 December 2009 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:19.49% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 5913.58% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$4.018 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 106$2.436 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$13.32 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 94$16.75 billion (31 December 2010 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$19.82 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 82$13.29 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$NACurrent account balance:-$3.067 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 150-$5.775 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$45.51 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 62$40.93 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:machinery and equipment, mineral products, chemicals, metals, textiles, foodstuffsExports - partners:Russia 35.4%, Netherlands 16.5%, Ukraine 12.1%, Latvia 7.1% (2012)Imports:$45.01 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 58$44.39 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:mineral products, machinery and equipment, chemicals, foodstuffs, metalsImports - partners:Russia 59.3%, Germany 5.9%, China 5.1%, Ukraine 5% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$5.809 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 87$6.011 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$34.12 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 68$34.02 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:Belarusian rubles (BYB/BYR) per US dollar -8,336.9 (2012 est.)4,974.6 (2011 est.)2,978.5 (2010 est.)2,789.49 (2009)2,130 (2008)Energy ::BelarusElectricity - production:28.55 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Electricity - consumption:29.54 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 61Electricity - exports:3.933 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 31Electricity - imports:8.404 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 27Electricity - installed generating capacity:8.032 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Electricity - from fossil fuels:99.7% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 54Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0.2% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 147Electricity - from other renewable sources:0.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Crude oil - production:30,000 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 66Crude oil - exports:34,320 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Crude oil - imports:431,300 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 18Crude oil - proved reserves:198 million bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Refined petroleum products - production:427,800 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Refined petroleum products - consumption:188,800 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 59Refined petroleum products - exports:302,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 23Refined petroleum products - imports:39,660 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Natural gas - production:220 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Natural gas - consumption:21.82 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 34Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 66Natural gas - imports:21.6 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 16Natural gas - proved reserves:2.832 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:68.24 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Communications ::BelarusTelephones - main lines in use:4.208 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 41Telephones - mobile cellular:10.695 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 71Telephone system:general assessment: Belarus lags behind its neighbors in upgrading telecommunications infrastructure; modernization of the network progressing with roughly two-thirds of switching equipment now digitaldomestic: state-owned Beltelcom is the sole provider of fixed-line local and long distance service; fixed-line teledensity is improving although rural areas continue to be underserved; multiple GSM mobile-cellular networks are experiencing rapid growth; mobile-cellular teledensity now exceeds 100 telephones per 100 personsinternational: country code - 375; Belarus is a member of the Trans-European Line (TEL), Trans-Asia-Europe (TAE) fiber-optic line, and has access to the Trans-Siberia Line (TSL); 3 fiber-optic segments provide connectivity to Latvia, Poland, Russia, and Ukraine; worldwide service is available to Belarus through this infrastructure; additional analog lines to Russia; Intelsat, Eutelsat, and Intersputnik earth stations (2008)Broadcast media:4 state-controlled national TV channels; Polish and Russian TV broadcasts are available in some areas; state-run Belarusian Radio operates 3 national networks and an external service; Russian and Polish radio broadcasts are available (2007)Internet country code:.byInternet hosts:295,217 (2012)country comparison to the world: 64Internet users:2.643 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 69Transportation ::BelarusAirports:65 (2013)country comparison to the world: 75Airports - with paved runways:total: 33over 3,047 m: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 201,524 to 2,437 m: 4914 to 1,523 m: 1under 914 m: 7 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 32over 3,047 m: 11,524 to 2,437 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 2under 914 m:28 (2013)Heliports:1 (2013)Pipelines:gas 5,386 km; oil 1,589 km; refined products 1,730 km (2013)Railways:total: 5,537 kmcountry comparison to the world: 32broad gauge: 5,512 km 1.520-m gauge (874 km electrified)standard gauge: 25 km 1.435-m gauge (2008)Roadways:total: 86,392 kmcountry comparison to the world: 55paved: 74,651 kmunpaved: 11,741 km (2010)Waterways:2,500 km (use limited by its location on the perimeter of the country and by its shallowness) (2011)country comparison to the world: 36Ports and terminals:river port(s): Mazyr (Prypyats')Military ::BelarusMilitary branches:Belarus Armed Forces: Land Force, Air and Air Defense Force, Special Operations Force (2013)Military service age and obligation:18-27 years of age for compulsory military service; conscript service obligation is 12-18 months, depending on academic qualifications; 17 year olds are eligible to become cadets at military higher education institutes, where they are classified as military personnel (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 2,401,785females age 16-49: 2,429,653 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 1,693,626females age 16-49: 2,012,401 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 51,855female: 48,760 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:1.4% of GDP (2005 est.)country comparison to the world: 105Transnational Issues ::BelarusDisputes - international:boundary demarcated with Latvia and Lithuania; Poland seeks enhanced demarcation and security along this Schengen hard border with financial assistance from the EURefugees and internally displaced persons:stateless persons: 6,969 (2012)Trafficking in persons:current situation: Belarus is a source, transit, and destination country for women, men, and children subjected to sex trafficking and forced labor; women and children are trafficked to European and Middle Eastern countries and within Belarus for sexual exploitation; Belarusian men, women, and children are found in forced labor in the construction industry and other sectors in Russia and Belarus; Belarusian men seeking work abroad are increasingly subjected to forced labortier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - Belarus does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; the government demonstrates decreased law enforcement efforts, conducting fewer trafficking investigations and convicting only one trafficking offender; while two new anti-trafficking laws were passed, they have not been fully implemented and government services to victims remain very limited; the government continues its efforts to prevent trafficking through public awareness campaigns and NGO-operated anti-trafficking hotlines (2013)Illicit drugs:limited cultivation of opium poppy and cannabis, mostly for the domestic market; transshipment point for illicit drugs to and via Russia, and to the Baltics and Western Europe; a small and lightly regulated financial center; anti-money-laundering legislation does not meet international standards and was weakened further when know-your-customer requirements were curtailed in 2008; few investigations or prosecutions of money-laundering activities (2008)"
Introduction ::BelarusBackground:After seven decades as a constituent republic of the USSR, Belarus attained its independence in 1991. It has retained closer political and economic ties to Russia than any of the other former Soviet republics. Belarus and Russia signed a treaty on a two-state union on 8 December 1999 envisioning greater political and economic integration. Although Belarus agreed to a framework to carry out the accord, serious implementation has yet to take place. Since his election in July 1994 as the country's first president, Aleksandr LUKASHENKO has steadily consolidated his power through authoritarian means. Government restrictions on freedom of speech and the press, peaceful assembly, and religion remain in place.Geography ::BelarusLocation:Eastern Europe, east of PolandGeographic coordinates:53 00 N, 28 00 EArea:total: 207,600 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 86land: 202,900 sq kmwater: 4,700 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly smaller than KansasLand boundaries:total: 3,306 kmborder countries: Latvia 171 km, Lithuania 680 km, Poland 605 km, Russia 959 km, Ukraine 891 kmCoastline:0 km (landlocked)Maritime claims:none (landlocked)Climate:cold winters, cool and moist summers; transitional between continental and maritimeTerrain:generally flat and contains much marshlandElevation extremes:lowest point: Nyoman River 90 mhighest point: Dzyarzhynskaya Hara 346 mNatural resources:timber, peat deposits, small quantities of oil and natural gas, granite, dolomitic limestone, marl, chalk, sand, gravel, clayLand use:arable land: 26.63%permanent crops: 0.59%other: 72.78% (2011)Irrigated land:1,150 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:58 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 4.34 cu km/yr (32%/65%/3%)per capita: 435.4 cu m/yr (2009)Natural hazards:NAEnvironment - current issues:soil pollution from pesticide use; southern part of the country contaminated with fallout from 1986 nuclear reactor accident at Chornobyl' in northern UkraineEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:landlocked; glacial scouring accounts for the flatness of Belarusian terrain and for its 11,000 lakesPeople and Society ::BelarusNationality:noun: Belarusian(s)adjective: BelarusianEthnic groups:Belarusian 83.7%, Russian 8.3%, Polish 3.1%, Ukrainian 1.7%, other 3.2% (2009 census)Languages:Belarusian (official) 23.4%, Russian (official) 70.2%, other 6.4% (includes small Polish- and Ukrainian-speaking minorities) (1999 census)Religions:Eastern Orthodox 80%, other (including Roman Catholic, Protestant, Jewish, and Muslim) 20% (1997 est.)Population:9,625,888 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 90Age structure:0-14 years: 15.2% (male 752,536/female 710,384)15-24 years: 12.3% (male 607,877/female 575,827)25-54 years: 45.5% (male 2,146,332/female 2,238,033)55-64 years: 13% (male 548,170/female 699,780)65 years and over: 14% (male 423,287/female 923,662) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 41.1 %youth dependency ratio: 21.6 %elderly dependency ratio: 19.5 %potential support ratio: 5.1 (2013)Median age:total: 39.2 yearsmale: 36.1 yearsfemale: 42.2 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:-0.18% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 211Birth rate:10.99 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 175Death rate:13.68 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 13Net migration rate:0.85 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Urbanization:urban population: 75% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 0.21% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:MINSK (capital) 1.861 million (2011)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.96 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.78 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.46 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.87 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:24.9 (2010 est.)Maternal mortality rate:190 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 58Infant mortality rate:total: 3.67 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 206male: 4.1 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 3.22 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 71.81 yearscountry comparison to the world: 140male: 66.14 yearsfemale: 77.82 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:1.46 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 193Contraceptive prevalence rate:72.6% (2005)Health expenditures:5.6% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 119Physicians density:4.87 physicians/1,000 population (2007)Hospital bed density:11.1 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 99% of populationtotal: 100% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 1% of populationtotal: 0% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 91% of populationrural: 97% of populationtotal: 93% of populationunimproved:urban: 9% of populationrural: 3% of populationtotal: 7% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.3% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 82HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:17,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 82HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 1,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Obesity - adult prevalence rate:24.3% (2008)country comparison to the world: 65Children under the age of 5 years underweight:1.3% (2005)country comparison to the world: 126Education expenditures:5.3% of GDP (2011)country comparison to the world: 62Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 99.6%male: 99.8%female: 99.5% (2009 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 15 yearsmale: 15 yearsfemale: 16 years (2011)Child labor - children ages 5-14:total number: 54,218percentage: 5 % (2005 est.)Government ::BelarusCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Belarusconventional short form: Belaruslocal long form: Respublika Byelarus'local short form: Byelarus'former: Belorussian (Byelorussian) Soviet Socialist RepublicGovernment type:republic in name, although in fact a dictatorshipCapital:name: Minskgeographic coordinates: 53 54 N, 27 34 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)daylight saving time: none scheduled for 2013Administrative divisions:6 provinces (voblastsi, singular - voblasts') and 1 municipality* (horad); Brest, Homyel' (Gomel), Horad Minsk* (Minsk City), Hrodna (Grodno), Mahilyow (Mogilev), Minsk, Vitsyebsk (Vitebsk)note: administrative divisions have the same names as their administrative centers; Russian spelling provided for reference when different from BelarusianIndependence:25 August 1991 (from the Soviet Union)National holiday:Independence Day, 3 July (1944); note - 3 July 1944 was the date Minsk was liberated from German troops, 25 August 1991 was the date of independence from the Soviet UnionConstitution:15 March 1994; revised by national referendum 24 November 1996 giving the presidency greatly expanded powers; became effective 27 November 1996; revised again 17 October 2004 removing presidential term limitsLegal system:civil law system; note - nearly all major codes (civil, civil procedure, criminal, criminal procedure, family and labor) have been revised and came into force in 1999 or 2000International law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: president Aleksandr LUKASHENKO (since 20 July 1994); note - the US does not recognize the results of the 19 December 2010 elections under which the Central Election Commission of Belarus declared LUKASHENKO presidenthead of government: prime minister Mikhail MYASNIKOVICH (since 28 December 2010); first deputy prime minister Vladimir SEMASHKO (since December 2003)cabinet: Council of Ministers(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term; first election took place on 23 June and 10 July 1994; according to the 1994 constitution, the next election should have been held in 1999, however, Aleksandr LUKASHENKO extended his term to 2001 via a November 1996 referendum; subsequent election held on 9 September 2001; an October 2004 referendum ended presidential term limits and allowed the president to run in a third (19 March 2006) and fourth election (19 December 2010); prime minister and deputy prime ministers appointed by the presidentelection results: Aleksandr LUKASHENKO reelected president; percent of vote - Aleksandr LUKASHENKO 79.7%, Andrey SANNIKOV 2.6%, other candidates 17.7%; note - election marred by electoral fraudLegislative branch:bicameral national assembly or natsionalnoye sobraniye consists of the Council of the Republic or Sovet Respubliki (64 seats; 56 members elected by regional and Minsk city councils and 8 members appointed by the president, to serve four-year terms) and the Chamber of Representatives or Palata Predstaviteley (110 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms); note - the US does not recognize the legitimacy of the national assemblyelections: Palata Predstaviteley - last held on 23 September 2012 (next to be held September 2016); OSCE observers determined that the election was neither free nor impartial and that vote counting was problematic in a number of polling stations; pro-LUKASHENKO candidates won every seat with no opposition representation in the chamber; international observers determined that the previous election, on 28 September 2008, despite minor improvements also fell short of democratic standards, with pro-LUKASHENKO candidates winning every seatelection results: Sovet Respubliki - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; Palata Predstaviteley [2008] - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - KPB 6, AP 1, no affiliation 103; Palata Predstaviteley [2012] - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - KPB 3, AP 1, no affiliation 106Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the chairman, deputy chairman, and NA judges); Constitutional Court (consists of 12 judges including a chairman and deputy chairman)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the president with the consent of the Council of the Republic; judges initially appointed for 5 years and evaluated for life appointment; Constitutional Court judges - 6 appointed by the president and 6 elected by the Chamber of Representatives; term of judges is 11 years with an age limit of 70subordinate courts: regional, district, city, town, and military courtsPolitical parties and leaders:pro-government parties:Belarusian Agrarian Party or AP [Mikhail SHIMANSKY]Belarusian Patriotic Movement (Belarusian Patriotic Party) or BPR [Nikolay ULAKHOVICH, chairman]Communist Party of Belarus or KPB [Igor KARPENKO]Liberal Democratic Party or LDP [Sergey GAYDUKEVICH]Republican Party of Labor and Justice [Vasiliy ZADNEPRYANYY]opposition parties:Belarusian Christian Democracy Party [Pavel SEVERINETS] (unregistered)Belarusian Party of the Left ""Fair World"" [Sergey KALYAKIN]Belarusian Popular Front or BPF [Aleksey YANUKEVICH]Belarusian Social-Democratic Hramada [Stanislav SHUSHKEVICH]Belarusian Social Democratic Party Hramada (""Assembly"") or BSDPH [Irina VESHTARD]Belarusian Social Democratic Party People's Assembly (""Narodnaya Hramada"") [Nikolay STATKEVICH] (unregistered)Christian Conservative Party or BPF [Zyanon PAZNIAK]European Belarus Campaign [Andrey SANNIKOV]Party of Freedom and Progress [Vladimir NOVOSYAD] (unregistered)""Tell the Truth"" Campaign [Vladimir NEKLYAYEV]United Civic Party or UCP [Anatoliy LEBEDKO]Political pressure groups and leaders:Assembly of Pro-Democratic NGOs (unregistered) [Sergey MATSKEVICH]Belarusian Congress of Democratic Trade Unions [Aleksandr YAROSHUK]Belarusian Association of Journalists [Zhana LITVINA]Belarusian Helsinki Committee [Aleh HULAK]Belarusian Independence Bloc (unregistered) and For Freedom movement [Aleksandr MILINKEVICH]Belarusian Organization of Working Women [Irina ZHIKHAR]BPF-Youth [Andrus KRECHKA]Charter 97 (unregistered) [Andrey SANNIKOV]Perspektiva small business association [Anatol SHUMCHENKO]Nasha Vyasna (unregistered) (""Our Spring"") human rights center [Ales BYALYATSKI]""Tell the Truth"" Movement [Vladimir NEKLYAYEV]Women's Independent Democratic Movement [Ludmila PETINA]Young Belarus (Malady Belarus) [Zmitser KASPYAROVICH]Youth Front (Malady Front) [Zmitser DASHKEVICH]International organization participation:BSEC (observer), CBSS (observer), CEI, CIS, CSTO, EAEC, EAPC, EBRD, FAO, GCTU, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, NSG, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, PFP, SCO (dialogue member), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer), ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Oleg KRAVCHENKOchancery: 1619 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20009telephone: [1] (202) 986-1604FAX: [1] (202) 986-1805consulate(s) general: New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Ethan GOLDRICHembassy: 46 Starovilenskaya Street, Minsk 220002mailing address: PSC 78, Box B Minsk, APO 09723telephone: [375] (17) 210-12-83FAX: [375] (17) 234-7853Flag description:red horizontal band (top) and green horizontal band one-half the width of the red band; a white vertical stripe on the hoist side bears Belarusian national ornamentation in red; the red band color recalls past struggles from oppression, the green band represents hope and the many forests of the countryNational symbol(s):mounted knight known as Pahonia (the Chaser)National anthem:name: ""My, Bielarusy"" (We Belarusians)lyrics/music: Mikhas KLIMKOVICH and Uladzimir KARYZNA/Nester SAKALOUSKInote: music adopted 1955, lyrics adopted 2002; after the fall of the Soviet Union, Belarus kept the music of its Soviet-era anthem but adopted new lyrics; also known as ""Dziarzauny himn Respubliki Bielarus"" (State Anthem of the Republic of Belarus)Economy ::BelarusEconomy - overview:As part of the former Soviet Union, Belarus had a relatively well-developed industrial base; it retained this industrial base - which is now outdated, energy inefficient, and dependent on subsidized Russian energy and preferential access to Russian markets - following the breakup of the USSR. The country also has a broad agricultural base which is inefficient and dependent on government subsidies. After an initial burst of capitalist reform from 1991-94, including privatization of state enterprises, creation of institutions of private property, and development of entrepreneurship, Belarus' economic development greatly slowed. About 80% of all industry remains in state hands, and foreign investment has been hindered by a climate hostile to business. A few banks, which had been privatized after independence, were renationalized. State banks account for 75% of the banking sector. Economic output, which had declined for several years following the collapse of the Soviet Union, revived in the mid-2000s thanks to the boom in oil prices. Belarus has only small reserves of crude oil, though it imports most of its crude oil and natural gas from Russia at prices substantially below the world market. Belarus exported refined oil products at market prices produced from Russian crude oil purchased at a steep discount. In late 2006, Russia began a process of rolling back its subsidies on oil and gas to Belarus. Tensions over Russian energy reached a peak in 2010, when Russia stopped the export of all subsidized oil to Belarus save for domestic needs. In December 2010, Russia and Belarus reached a deal to restart the export of discounted oil to Belarus. Little new foreign investment has occurred in recent years. In 2011, a financial crisis began, triggered by government directed salary hikes unsupported by commensurate productivity increases. The crisis was compounded by an increased cost in Russian energy inputs and an overvalued Belarusian ruble, and eventually led to a near three-fold devaluation of the Belarusian ruble in 2011. In November 2011, Belarus agreed to sell to Russia its remaining shares in Beltransgaz, the Belarusian natural gas pipeline operator, in exchange for reduced prices for Russian natural gas. Receiving more than half of a $3 billion loan from the Russian-dominated Eurasian Economic Community Bail-out Fund, a $1 billion loan from the Russian state-owned bank Sberbank, and the $2.5 billion sale of Beltranzgas to Russian state-owned Gazprom helped stabilize the situation in 2012; nevertheless, the Belarusian currency lost more than 60% of its value, as the rate of inflation reached 53% in 2011 and 59% in 2012.GDP (purchasing power parity):$149.2 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 63$147 billion (2011 est.)$139.2 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$63.26 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:1.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1475.5% (2011 est.)7.7% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$15,900 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 85$15,600 (2011 est.)$14,700 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:31.6% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2029.2% of GDP (2011 est.)26.2% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 46.7%government consumption: 14.6%investment in fixed capital: 32.8%investment in inventories: 1.6%exports of goods and services: 81.6%imports of goods and services: -77.1%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 9.1%industry: 47.2%services: 43.7% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:grain, potatoes, vegetables, sugar beets, flax; beef, milkIndustries:metal-cutting machine tools, tractors, trucks, earthmovers, motorcycles, televisions, synthetic fibers, fertilizer, textiles, radios, refrigeratorsIndustrial production growth rate:4% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Labor force:5 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 76Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 9.4%industry: 45.9%services: 44.7% (2005 est.)Unemployment rate:1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 71.6% (2005)note: official registered unemployed; large number of underemployed workersPopulation below poverty line:27.1% (2003 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 3.8%highest 10%: 21.9% (2008)Distribution of family income - Gini index:27.2 (2008)country comparison to the world: 12521.7 (1998)Budget:revenues: $22.38 billionexpenditures: $21.96 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:35.4% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):0.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 34Public debt:31.5% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 11448.5% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):59.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 22353.3% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:10.5% (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 1413.5% (31 December 2009 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:19.49% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 5913.58% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$4.018 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 106$2.436 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$13.32 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 94$16.75 billion (31 December 2010 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$19.82 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 82$13.29 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$NACurrent account balance:-$3.067 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 150-$5.775 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$45.51 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 62$40.93 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:machinery and equipment, mineral products, chemicals, metals, textiles, foodstuffsExports - partners:Russia 35.4%, Netherlands 16.5%, Ukraine 12.1%, Latvia 7.1% (2012)Imports:$45.01 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 58$44.39 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:mineral products, machinery and equipment, chemicals, foodstuffs, metalsImports - partners:Russia 59.3%, Germany 5.9%, China 5.1%, Ukraine 5% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$5.809 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 87$6.011 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$34.12 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 68$34.02 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:Belarusian rubles (BYB/BYR) per US dollar -8,336.9 (2012 est.)4,974.6 (2011 est.)2,978.5 (2010 est.)2,789.49 (2009)2,130 (2008)Energy ::BelarusElectricity - production:28.55 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Electricity - consumption:29.54 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 61Electricity - exports:3.933 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 31Electricity - imports:8.404 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 27Electricity - installed generating capacity:8.032 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Electricity - from fossil fuels:99.7% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 54Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0.2% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 147Electricity - from other renewable sources:0.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Crude oil - production:30,000 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 66Crude oil - exports:34,320 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Crude oil - imports:431,300 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 18Crude oil - proved reserves:198 million bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Refined petroleum products - production:427,800 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Refined petroleum products - consumption:188,800 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 59Refined petroleum products - exports:302,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 23Refined petroleum products - imports:39,660 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Natural gas - production:220 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Natural gas - consumption:21.82 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 34Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 66Natural gas - imports:21.6 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 16Natural gas - proved reserves:2.832 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:68.24 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Communications ::BelarusTelephones - main lines in use:4.208 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 41Telephones - mobile cellular:10.695 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 71Telephone system:general assessment: Belarus lags behind its neighbors in upgrading telecommunications infrastructure; modernization of the network progressing with roughly two-thirds of switching equipment now digitaldomestic: state-owned Beltelcom is the sole provider of fixed-line local and long distance service; fixed-line teledensity is improving although rural areas continue to be underserved; multiple GSM mobile-cellular networks are experiencing rapid growth; mobile-cellular teledensity now exceeds 100 telephones per 100 personsinternational: country code - 375; Belarus is a member of the Trans-European Line (TEL), Trans-Asia-Europe (TAE) fiber-optic line, and has access to the Trans-Siberia Line (TSL); 3 fiber-optic segments provide connectivity to Latvia, Poland, Russia, and Ukraine; worldwide service is available to Belarus through this infrastructure; additional analog lines to Russia; Intelsat, Eutelsat, and Intersputnik earth stations (2008)Broadcast media:4 state-controlled national TV channels; Polish and Russian TV broadcasts are available in some areas; state-run Belarusian Radio operates 3 national networks and an external service; Russian and Polish radio broadcasts are available (2007)Internet country code:.byInternet hosts:295,217 (2012)country comparison to the world: 64Internet users:2.643 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 69Transportation ::BelarusAirports:65 (2013)country comparison to the world: 75Airports - with paved runways:total: 33over 3,047 m: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 201,524 to 2,437 m: 4914 to 1,523 m: 1under 914 m: 7 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 32over 3,047 m: 11,524 to 2,437 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 2under 914 m:28 (2013)Heliports:1 (2013)Pipelines:gas 5,386 km; oil 1,589 km; refined products 1,730 km (2013)Railways:total: 5,537 kmcountry comparison to the world: 32broad gauge: 5,512 km 1.520-m gauge (874 km electrified)standard gauge: 25 km 1.435-m gauge (2008)Roadways:total: 86,392 kmcountry comparison to the world: 55paved: 74,651 kmunpaved: 11,741 km (2010)Waterways:2,500 km (use limited by its location on the perimeter of the country and by its shallowness) (2011)country comparison to the world: 36Ports and terminals:river port(s): Mazyr (Prypyats')Military ::BelarusMilitary branches:Belarus Armed Forces: Land Force, Air and Air Defense Force, Special Operations Force (2013)Military service age and obligation:18-27 years of age for compulsory military service; conscript service obligation is 12-18 months, depending on academic qualifications; 17 year olds are eligible to become cadets at military higher education institutes, where they are classified as military personnel (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 2,401,785females age 16-49: 2,429,653 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 1,693,626females age 16-49: 2,012,401 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 51,855female: 48,760 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:1.4% of GDP (2005 est.)country comparison to the world: 105Transnational Issues ::BelarusDisputes - international:boundary demarcated with Latvia and Lithuania; Poland seeks enhanced demarcation and security along this Schengen hard border with financial assistance from the EURefugees and internally displaced persons:stateless persons: 6,969 (2012)Trafficking in persons:current situation: Belarus is a source, transit, and destination country for women, men, and children subjected to sex trafficking and forced labor; women and children are trafficked to European and Middle Eastern countries and within Belarus for sexual exploitation; Belarusian men, women, and children are found in forced labor in the construction industry and other sectors in Russia and Belarus; Belarusian men seeking work abroad are increasingly subjected to forced labortier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - Belarus does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; the government demonstrates decreased law enforcement efforts, conducting fewer trafficking investigations and convicting only one trafficking offender; while two new anti-trafficking laws were passed, they have not been fully implemented and government services to victims remain very limited; the government continues its efforts to prevent trafficking through public awareness campaigns and NGO-operated anti-trafficking hotlines (2013)Illicit drugs:limited cultivation of opium poppy and cannabis, mostly for the domestic market; transshipment point for illicit drugs to and via Russia, and to the Baltics and Western Europe; a small and lightly regulated financial center; anti-money-laundering legislation does not meet international standards and was weakened further when know-your-customer requirements were curtailed in 2008; few investigations or prosecutions of money-laundering activities (2008)"
The World Factbook. 2014.
